By Sunita Arnold, Nov 2, 2023

Table of Contents
Imagine investing in the next billion-dollar company just before it goes public, reaping the rewards of lower initial valuations and significant growth potential. Pre-IPO investing offers such opportunities, allowing investors to get in on the ground floor of promising companies before they hit the stock exchange. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about how to buy pre-IPO stock.
Pre-IPO stocks represent shares of private companies sold to investors before they go public through an initial public offering (IPO). Pre-IPO markets are mostly dominated by institutional investors, venture capitalists, and accredited investors, which sometimes makes it challenging for non-accredited investors to participate.
A pre-IPO stock refers to the shares of a company that are available to private investors prior to the company’s initial public offering and listing on a public exchange such as NYSE, NASDAQ, or LSE, for example. The intricacies of investing in these stocks demand a robust understanding of the market, and careful consideration of the available financial information and the associated risks.
The pre-IPO market landscape is an exclusive space, brimming with unique opportunities and challenges. Here, we’ll deep dive into understanding the dynamics of the pre-IPO landscape, how it operates, the key players involved, and what you need to know as an investor navigating this market.

To invest in pre-IPO stocks, there are three main methods: private equity investment platforms, direct purchases from companies, and indirect investments. Each method presents unique advantages and challenges. Consequently, investors need to weigh their options and select an approach that aligns with their investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Direct engagement with companies to purchase shares is another route. This method often involves a more hands-on approach, allowing for a deeper personal assessment and direct communication with the company. However, it also necessitates an acute awareness of the regulatory environment and a strong due diligence process, considering the lack of intermediary oversight.
Indirect investments offer another avenue, where investors can gain exposure to pre-IPO companies by investing in funds or other financial instruments that hold pre-IPO shares. This method could dilute the direct impact of the investment on an investor’s portfolio and might involve additional complexities and fees, but it also offers a more diversified approach to pre-IPO investment.
Step into the high-reward world of private equities. Don’t wait, your portfolio expansion starts here!
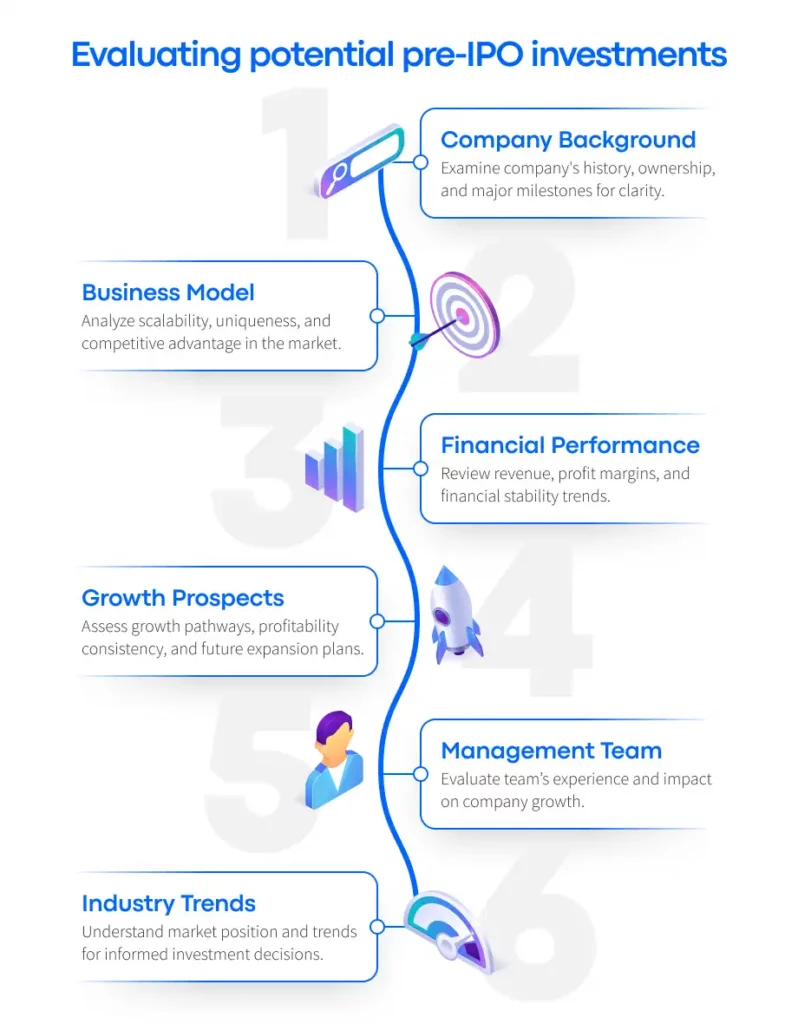
When evaluating potential pre-IPO investments, comprehensive research is a necessity. Investors should assess the company’s background, financial performance, and management team to ensure the investment aligns with their goals and risk tolerance. Analyzing these factors enables investors to make informed decisions about pursuing a potential pre-IPO investment opportunity.
To evaluate a potential pre-IPO investment, start by understanding the company’s background, including its founding, ownership, and key milestones. Analyzing the viability, scalability, and uniqueness of the company’s business model in its competitive landscape is crucial. Investors should assess whether the company has a clear strategy, a compelling value proposition, and a sustainable competitive advantage.
Next, assess the financial performance, growth prospects, and potential risks of the prospective company. Dive into available financial statements and analytics to understand the company’s revenue streams, profit margins, growth trajectories, and customer acquisition costs. Look for consistency, profitability, and a clear pathway to future growth. A strong financial footing and a clear, viable future growth plan are positive indicators, but any inconsistencies, lack of profitability, or unclear growth strategies should be viewed with caution.
Evaluating the management team’s experience, industry trends, and the company’s position within the market is essential for assessing a potential pre-IPO investment. A strong management team with a track record of success can significantly impact the company’s growth potential.
Additionally, understanding industry trends and the company’s market position can provide valuable insights into its potential for success, helping investors make informed decisions about whether to pursue a pre-IPO investment opportunity.
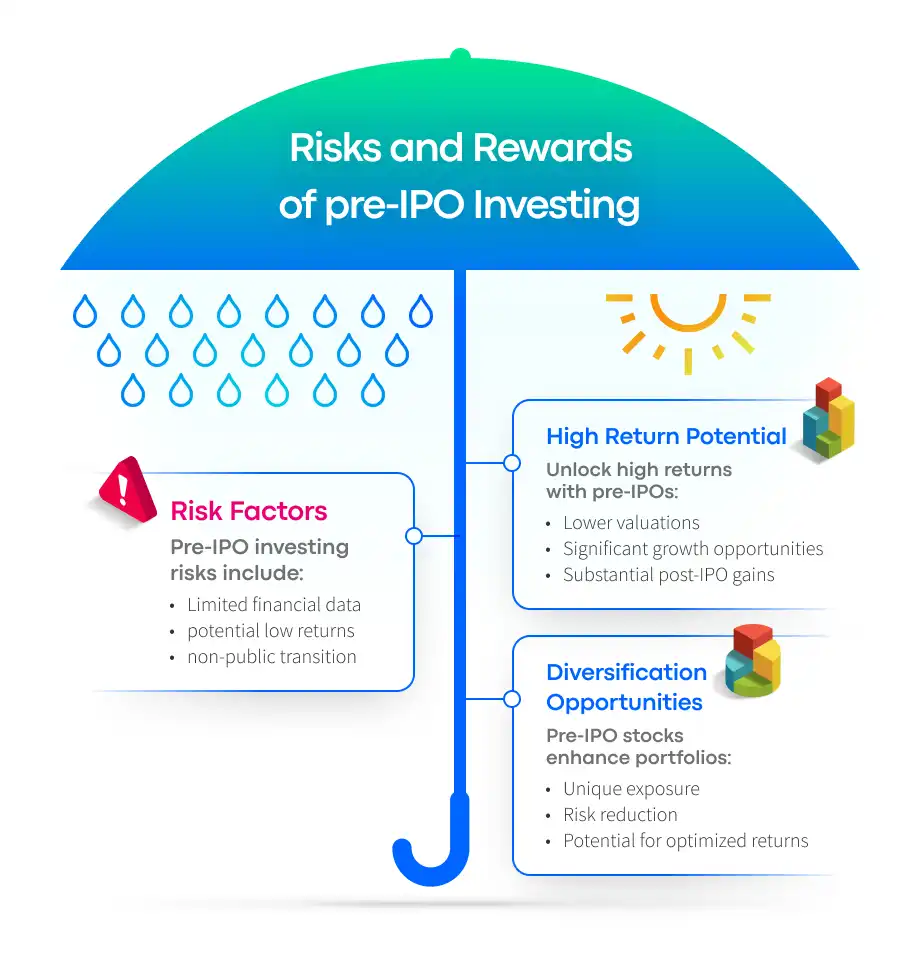
Pre-IPO investing presents opportunities for high returns, diversification, and comes with various risk factors. While the potential for rapid growth and exponential returns can make pre-IPO investing attractive, it is crucial for pre-IPO investors to consider the associated risks and ensure the investment aligns with their goals and risk tolerance.
Pre-IPO investments can yield high returns due to lower initial valuations and potential for significant growth. Companies at the pre-IPO stage often have a lower market value than publicly traded companies, providing investors with the opportunity to acquire shares at a discounted price. If the company performs well after its IPO, investors who bought pre-IPO shares may see substantial returns on their investment.
Investing in pre-IPO stocks can provide diversification benefits by adding exposure to private companies in an investor’s portfolio. Diversification is a strategy employed by investors to distribute their investments across various asset classes, sectors, and industries in order to reduce risk and optimize returns.
By including pre-IPO stocks in their investment portfolio, investors can potentially reduce the overall risk of their investments and enhance their long-term returns.
Risks associated with pre-IPO investing include lack of financial information, potential for low returns, and the possibility that the company may not go public. Since pre-IPO companies are still private, there may be limited financial information available, making it difficult for investors to make informed decisions. Additionally, if the company underperforms after its IPO or never goes public, investors may not see the expected returns on their investment or may even lose their initial investment.
Share Your Insights: Have thoughts or experiences to share on this topic? Dive into the discussion and leave your insights in the comments section below!
Leverage the power of private equities. Make your move and accelerate your wealth creation journey today!
Pre-IPO placements are a common method used by companies to sell pre-IPO stock options before going public. This involves offering shares to private investors, which could include institutional investors, family offices, and high-net-worth individuals, before they are available to the general public through an IPO. Pre-IPO placements allow companies to raise significant capital to support their growth and expansion plans. These placements are often attractive to investors due to the potential for purchasing shares at a lower price before the company gets listed on a public exchange, where the stock price may increase.
Stock options are another avenue through which companies can engage investors and employees before going public. Companies may offer stock options as part of employee compensation packages or to external investors. Stock options give the holder the right to buy company stocks at a predetermined price, usually referred to as the “exercise” or “strike” price, within a specified timeframe. Offering pre-IPO stock options can be a strategic move for companies, fostering a sense of ownership and alignment among employees and early investors with the company’s long-term success. For investors and employees, stock options present an opportunity to capitalize on the company’s success if the public listing increases the stock’s market price above the option’s exercise price.
Venture capital and angel investors play an important role in a company’s pre-IPO fundraising stage. Venture capitalists are professional groups that manage pooled funds from many investors to invest in startups and small businesses. They not only bring capital but often also offer guidance and expertise to help the business grow. On the other hand, angel investors are affluent individuals who provide capital for a business start-up, usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity. Engaging with venture capitalists and angel investors allows companies to access the necessary capital and mentorship needed to scale their operations and navigate the path to a potential successful IPO. These investors typically aim to exit their investment profitably once the company goes public.
Investing in pre-IPO stocks necessitates a clear understanding and adherence to certain accreditation and eligibility requirements. These guidelines have been put in place to safeguard the interests of investors and ensure that they possess the financial acumen and stability required to navigate the complexities of the pre-IPO investment landscape.
The criteria for achieving this status can vary based on jurisdiction and regulatory authorities. Generally speaking, accredited investors are distinguished by their substantial income, significant net worth, or specialized professional expertise, enabling them to embark on investment ventures that are not registered with regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Attaining the status of an accredited investor unveils a multitude of investment opportunities, including the prospect of participating in pre-IPO investments, thus broadening one’s investment horizon.
Investors aiming to participate in pre-IPO investments are often met with a series of eligibility prerequisites, such as meeting minimum investment thresholds, adhering to stipulated lock-in periods, and complying with various other regulatory stipulations. These criteria may encompass considerations such as the requisite minimum investment amounts, which may vary across different pre-IPO platforms or brokerage entities. For instance, certain platforms might necessitate a preliminary investment outlay, which could be in the ballpark of $100,000 or more.
Moreover, investors might encounter lock-in periods, during which they are restricted from divesting their shares for a predetermined duration. Such mechanisms are instituted to foster investment stability and mitigate the implications of precipitous sell-offs. A comprehensive understanding and adherence to these eligibility benchmarks are instrumental in facilitating investors’ seamless navigation through the intricate terrains of the pre-IPO investment domain, enabling them to strategically position themselves to capitalize on emergent investment opportunities.
In conclusion, pre-IPO investing offers the potential for high returns, diversification opportunities, and exposure to private companies before they become publicly traded. By understanding the pre-IPO market landscape, navigating accreditation and eligibility requirements, and exploring top pre-IPO investing platforms and brokers, investors can make informed decisions about whether to pursue this unique investment opportunity. As with any investment, it is essential to conduct thorough research and carefully consider the associated risks and rewards before diving into the world of pre-IPO investing.
This material, provided by Linqto, is for informational purposes only and is not intended as investment advice or any form of professional guidance. Before making any investment decision, especially in the dynamic field of private markets, it is recommended that you seek advice from professional advisors. The information contained herein does not imply endorsement of any third parties or investment opportunities mentioned. Our market views and investment insights are subject to change and may not always reflect the most current developments. No assumption should be made regarding the profitability of any securities, sectors, or markets discussed. Past performance is not indicative of future results, and investing in private markets involves unique risks, including the potential for loss. Historical and hypothetical performance figures are provided to illustrate possible market behaviors and should not be relied upon as predictions of future performance.
Can anyone buy pre-IPO stock?
Not everyone has the privilege to invest in pre-IPO stocks. While theoretically, anyone can participate in pre-IPO investments, in practice, access is typically reserved for qualified investors such as accredited investors, angel investors, or those engaging through specialized brokers in secondary marketplaces. Such investors have to meet certain financial and regulatory criteria, ensuring they have the necessary expertise and financial resilience to navigate the complexities and risks inherent in pre-IPO investments.
Is it worth buying pre-IPO shares?
Investing in pre-IPO shares can be enticing, offering the prospect of substantial returns by gaining early access to a potentially promising company. For investors, pre-IPO investments can be a strategic way to diversify their portfolios with allocations to burgeoning startups. However, investing in pre-IPO shares also carries inherent risks and complexities. It is imperative for investors to diligently scrutinize the Private Placement Memorandum (PPM) and undertake a meticulous evaluation of the long-term prospects and potential hurdles of the investment. Consultation with financial advisors is advisable to garner personalized insights and to adeptly integrate private company stocks into one’s investment portfolio, aligning with individual financial objectives and risk tolerances.
How much are pre-IPO shares worth?
The valuation of pre-IPO shares is a nuanced process, contingent on a fair value estimation of the company. Prior to the IPO, the worth of pre-IPO shares is deduced based on rigorous assessments and appraisals of the company’s overall financial health, market position, and growth prospects. Post-IPO, the value of the shares can be more transparently ascertained based on market prices, but investors interested in pre-IPO shares must primarily rely on the company’s fair value estimations and undertake comprehensive due diligence.
How to buy an IPO?
Participation in an IPO is facilitated through brokerage platforms. Interested investors should commence by ensuring that they possess a brokerage account and meet the requisite eligibility benchmarks. The process unfolds by expressing an ‘Indication of Interest’ (IOI), following which investors can request and place orders for shares. Key eligibility criteria may encompass having a minimum account value, which could be around $250,000, or having executed a certain threshold of trades, possibly 30 trades within the preceding three months. It is important for investors to be apprised of the specific eligibility prerequisites and processes stipulated by their respective brokerage platforms to adeptly navigate the IPO participation process.
2 Comments
I would like to know how I can get into a Re-IPO stock of interest.
But how